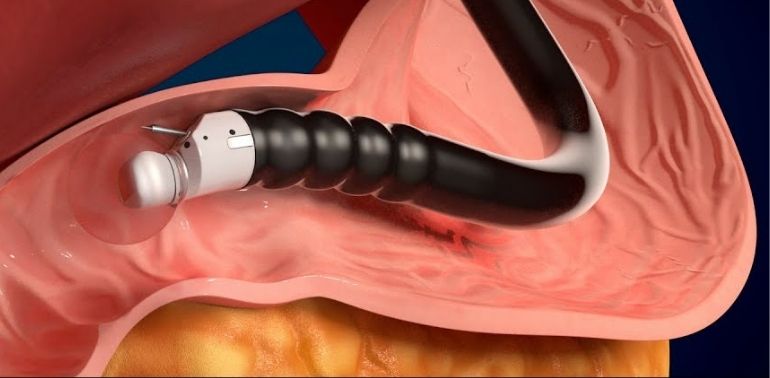
What is EUS-Guided Intervention?
EUS-guided intervention is a procedure in which endoscopic ultrasound is used to visualize internal structures and guide therapeutic interventions. By using the ultrasound imaging obtained through the endoscope, your doctor can perform a variety of treatments with high precision, often in areas that are difficult to access with conventional methods.
Common EUS-guided interventions include:
- Needle Biopsy: Collecting tissue samples for analysis from organs like the pancreas or liver.
- Cyst Drainage: Draining fluid-filled cysts or abscesses in the pancreas or bile ducts.
- Drain Placement: Inserting stents or drains into blocked ducts or bile systems.
- Tumor Ablation: Targeting and treating tumors in the pancreas, bile ducts, or other areas.
- FNA (Fine Needle Aspiration): A specific technique for taking a tissue sample from a mass or lesion under EUS guidance.
By using EUS to guide interventions, doctors can achieve precise results with minimal risk of damage to surrounding tissues. EUS-guided procedures can often replace more invasive surgical techniques, resulting in faster recovery times and less discomfort.
Benefits of EUS-Guided Interventions
EUS-guided interventions offer several advantages over traditional surgical approaches:
- Minimally Invasive: Unlike surgery, EUS-guided interventions involve no incisions, reducing the risk of infection and shortening recovery time.
- Precision: The high-resolution imaging provided by EUS allows your gastroenterologist to target areas of concern with great accuracy, minimizing damage to surrounding organs or tissues.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Because the procedure is minimally invasive, the risk of complications such as bleeding or infection is significantly lower than with traditional surgery.
- Faster Recovery: Most EUS-guided interventions can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day and resume normal activities more quickly.
- Lower Cost: EUS-guided interventions are often more cost-effective than open surgery, as they typically require a shorter hospital stay and fewer post-operative care costs.
Common Conditions Treated with EUS-Guided Interventions
EUS-guided interventions are used to diagnose and treat a variety of digestive and gastrointestinal conditions. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Pancreatic Disorders
EUS is frequently used to evaluate and treat conditions affecting the pancreas, including:
- Pancreatic Cancer: EUS-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) or biopsy can provide tissue samples to help diagnose pancreatic cancer.
- Pancreatic Cysts: Fluid-filled cysts in the pancreas can be drained using EUS guidance, reducing the risk of infection or complications.
- Pancreatitis: EUS can identify underlying causes of chronic pancreatitis and help guide the placement of stents to relieve blockages.
2. Biliary Tract Obstructions
For patients with blockages in the bile ducts, EUS-guided interventions can be used to:
- Drain Gallbladder or Biliary Cysts: EUS can guide drainage of cysts, abscesses, or infected bile, helping relieve pressure and prevent further complications.
- Stent Placement: In cases of bile duct obstructions (such as those caused by tumors or strictures), a stent can be placed under EUS guidance to allow bile to flow freely again.
3. Liver Diseases
EUS is often used to assess liver health and treat conditions such as:
- Liver Cysts: Cysts in the liver can be drained or biopsied using EUS guidance.
- Liver Cancer: EUS-guided biopsy allows for accurate diagnosis and staging of liver cancers.
4. Gastrointestinal Tumors
EUS can help detect tumors in the gastrointestinal tract, especially in difficult-to-reach areas. The procedure can also be used to guide fine needle aspiration (FNA) or needle biopsy for cancer diagnosis.
5. Lymph Node Biopsy
EUS can also be used to evaluate enlarged lymph nodes and guide biopsies for diagnosis, especially in cases where lymphoma or metastatic cancer is suspected.

